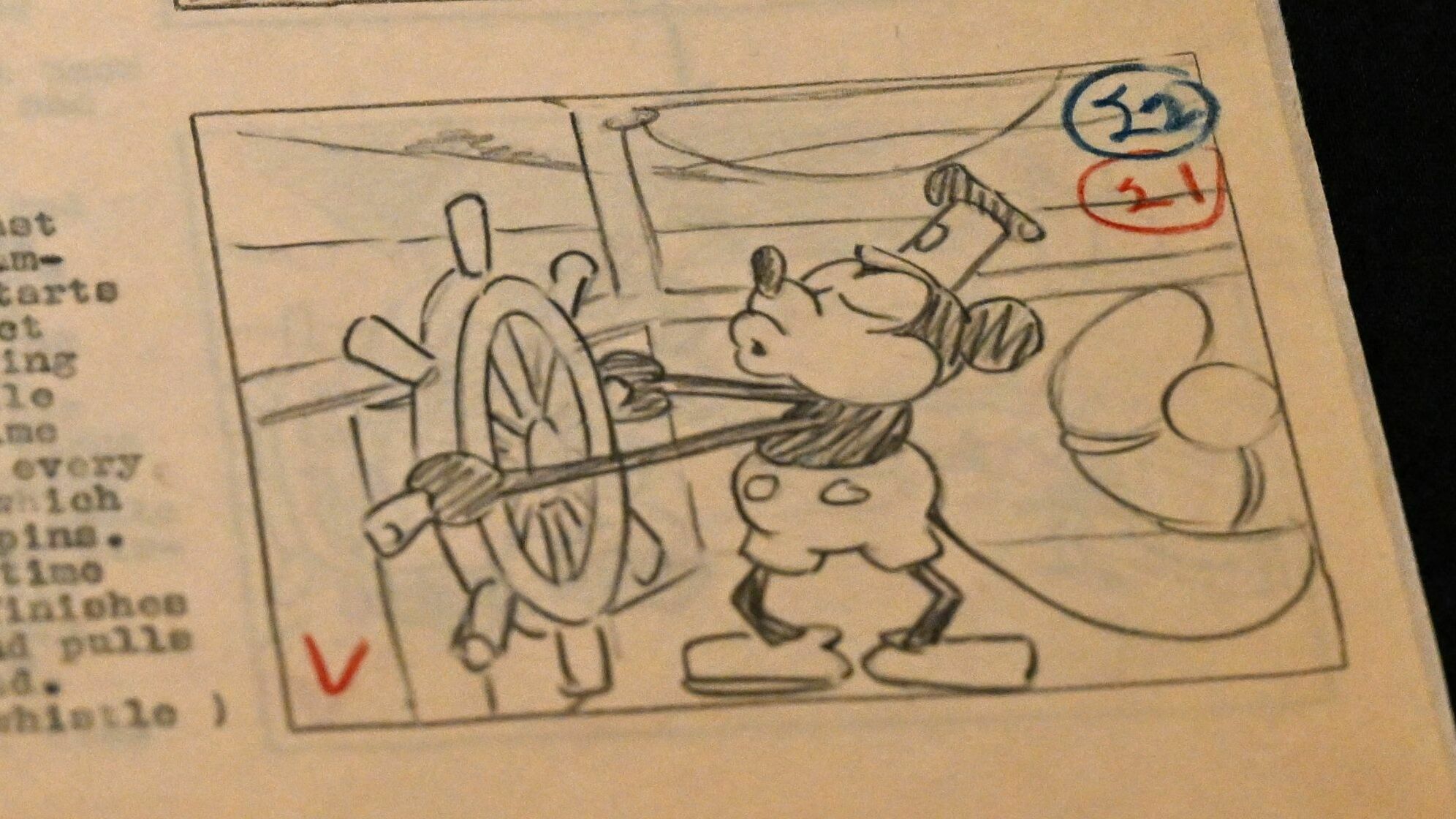
An early Walt Disney movie featuring the first appearance of Mickey Mouse is among the copyrighted works from 1928 moving into the public domain on Jan. 1, 2024.
But the cartoon creature who stars in the animated short Steamboat Willie isn’t a lot like the Mickey we know today. He’s more rascally and rough. His roots in the blackface minstrel shows of the time are more apparent.
And he’s not exactly cuddly. For much of the movie, Mickey amuses himself by forcing barnyard animals into being unwilling musical instruments.
News with a little more humanity
WPR’s “Wisconsin Today” newsletter keeps you connected to the state you love without feeling overwhelmed. No paywall. No agenda. No corporate filter.
“You know, he’s evolved so much and become more 3D and colorful,” observes Ryan Harmon, a former Disney Imagineer, of the character today. He remembers anxious talk, when he worked at the company in the 1990s, about the beloved icon eventually entering the public domain.
But that’s not happening, says Kembrew McLeod, a communications professor and intellectual property scholar at the University of Iowa.
“What is going into the public domain is this particular appearance in this particular film,” he says.
That means people can creatively reuse only the Mickey Mouse from Steamboat Willie. Not the Mickey Mouse in the 1940 movie Fantasia. Nor the one on Mickey Mouse Clubhouse, a kids’ show that aired on the Disney Channel for a decade starting in 2006.
New versions of Mickey Mouse remain under copyright. Copyright applies to creative characters, movies, books, plays, songs and more. And as it happens, Mickey Mouse is also trademarked.
“Trademark law is entirely about protecting brands, logos and names — like Mickey Mouse as a logo, or the name Mickey Mouse,” McLeod says.
“And of course, trademark law has no end,” adds Harvard Law School professor Ruth Okediji. Disney and other corporations, she says, use trademarks to extend control over intellectual property.” As long as the mark remains distinctive in the supply of goods and services, the owner of the trademark gets to protect that trademark.”
“It’s something copyright scholars like myself have been concerned about,” she continues. “This effective undermining of the public domain by allowing trademark law to effectively extend the life of a copyrighted work. And it’s my hope that either Congress or the courts will restore the full balance between the protection of creativity and the protection of the public domain, which is also the protection of creativity.”
Now, people should still be able to do things like incorporate clips of Steamboat Willie in an art project, or maybe sell a T-shirt reproducing a frame from the movie. But Okediji cautions if those things infringe on the trademark, or threaten to dilute the trademark because of the way it’s used, then Disney can use the law to assert its ownership.
This could keep people from making, for example, a Mickey Mouse slasher movie. Which someone actually did when Winnie the Pooh went into the public domain last year.
“You also can’t just call your restaurant Mickey Mouse on January 1st,” Okediji chuckles. “You can’t say, ‘I’m the Mickey Mouse restaurant.’ That would be a clear trademark violation.”
The Walt Disney Company has earned a reputation for aggressive litigiousness over such matters. In 1989, it threatened to sue, for example three Florida daycares for painting Disney characters in a mural on its walls.
But more recently, McLeod says, the company has turned its focus from copyright and trademark related lawsuits to curbing online piracy. It’s possible, he says, an old cartoon from 1928 may not be all that valuable in 2024. The company even made Steamboat Willie available on YouTube for free back in 2009.
“Here is the irony,” McCleod says. “Steamboat Willie is based on a popular film at the time.”
Steamboat Bill, Jr. was a Buster Keaton hit that came out earlier that year. Steamboat Willie is a play on its name.
“Mickey Mouse made an appearance in a film for the first time that very much relied on another copyrighted work that helped propel its popularity,” McLeod continues. “When you’re referring to something that’s popular, most likely it’s going to create wider audiences and audiences who are recognizing that that particular reference.”
As enshrined in the Constitution, he says, copyright was originally intended to protect creators for fewer than 30 years. While copyright extensions may enrich corporations, they impoverish the cultural conversations that rely on relevancy, innovation and creativity to drive artistic and technological progress.
9(MDAyMjQ1NTA4MDEyMjU5MTk3OTdlZmMzMQ004))
© Copyright 2025 by NPR. To see more, visit https://www.npr.org.9(MDAyMjQ1NTA4MDEyMjU5MTk3OTdlZmMzMQ004))